Schizophrenia: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Living With the Condition
Schizophrenia is one of the most misunderstood mental health disorders in the world. It affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves, often making it difficult for them to differentiate reality from imagination. According to global health estimates, schizophrenia affects 1 in every 300 people, making it a significant public health concern. Despite this, lack of awareness and social stigma prevent many from seeking timely help.
Understanding the various aspects of schizophrenia, including symptoms, is crucial for anyone affected by this condition.
This blog aims to provide a clear understanding of schizophrenia—its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and how individuals and families can manage the condition better.
What Is Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a chronic psychiatric disorder that impacts brain function. It interferes with a person’s ability to:
- Think clearly
- Manage emotions
- Make decisions
- Relate to others
- Perceive reality
It is not the same as “split personality,” a common misconception. Instead, schizophrenia involves distorted thinking, hallucinations, delusions, and impaired functioning.
Recognizing the schizophrenia symptoms allows for early intervention and better management.
The condition typically begins in late adolescence or early adulthood, although early signs may appear much earlier.
Common Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Symptoms of schizophrenia fall into three major categories: positive symptoms, negative symptoms, and cognitive symptoms.
Knowing the schizophrenia symptoms can help in identifying the disorder sooner.
- Positive Symptoms Positive symptoms of schizophrenia encompass a range of manifestations that indicate an excess or distortion of normal functions. These may include hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking, which significantly impact an individual’s perception of reality. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment, as they can severely disrupt daily functioning and social interactions. Comprehensive management strategies are essential to address these symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected.
These symptoms “add” abnormal behaviors. 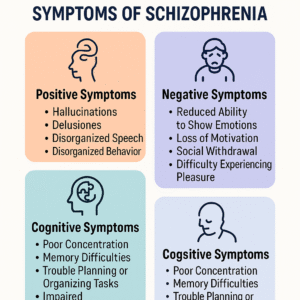
- Hallucinations: Hearing voices or seeing things that are not there.
- Delusions: False beliefs, such as feeling persecuted or believing one has special powers.
- Disorganized Speech: Speaking in ways that are confusing, disconnected, or difficult to understand.
- Disorganized Behavior: Unpredictable agitation, inappropriate emotional responses, or unusual movements.
- Negative Symptoms
These symptoms relate to a reduction in normal emotional and behavioral functions.
- Reduced ability to show emotions
- Loss of motivation
- Social withdrawal
- Difficulty experiencing pleasure
- Reduced speaking (alogia)
- Cognitive Symptoms
These symptoms affect thinking and problem-solving.
- Poor concentration
- Memory difficulties
- Trouble planning or organizing tasks
- Impaired decision-making
Cognitive symptoms often make daily activities like studying, working, or managing relationships challenging.
Learning about schizophrenia symptoms can empower families to provide better support.
What Causes Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia develops due to a combination of biological, genetic, and environmental factors. There is no single cause; instead, several influences interact to trigger the condition.
Understanding the underlying causes of schizophrenia symptoms is essential for effective treatment.
- Genetic Factors
If a person has a close family member with schizophrenia, their chances of developing the disorder increase. However, most people with a family history never develop it, indicating genes are just one part of the puzzle.
- Chemical Imbalance in the Brain
Neurotransmitters—especially dopamine and glutamate—play an important role in regulating mood and perception. Imbalances in these chemicals can contribute to schizophrenia symptoms.
Noticing changes in behavior can often lead to identifying schizophrenia symptoms early.
- Brain Structure Differences
Studies show that some individuals with schizophrenia have subtle differences in brain structure and functioning, although not all patients exhibit these changes.
- Environmental Triggers
Certain factors may increase risk, such as:
- Exposure to emotional trauma
- Prenatal infections
- Nutritional deficiencies during pregnancy
- Substance abuse, especially cannabis or hallucinogens
- Extreme stress during adolescence or early adulthood
Environmental factors do not cause schizophrenia alone but may trigger symptoms in someone already predisposed.
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing schizophrenia is a detailed process. There is no blood test or scan that can confirm the disorder. Instead, diagnosis is based on:
-
- Psychiatric evaluation
During evaluations, healthcare providers focus on schizophrenia symptoms to make a diagnosis.
- Observation of behavior
- Medical history
- Symptom duration (symptoms must persist for at least 6 months)
Doctors may also use brain imaging or lab tests to rule out other medical conditions, such as neurological disorders or substance-induced psychosis.
Early diagnosis is crucial, as treatment is more effective when started early.
Treatment Options for Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a lifelong condition, but with the right treatment, individuals can lead meaningful and productive lives. Treatment usually includes a combination of medication, therapy, and social support.
Effective treatment plans are built around understanding schizophrenia symptoms in depth.
- Medication
Most patients benefit from antipsychotic medications, which help reduce hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
Common types include:
- Atypical antipsychotics (newer medications)
- Typical antipsychotics (older medications)
These medications may take several weeks to show effects and sometimes cause side effects. A healthcare provider helps adjust doses for best results.
-
- Psychotherapy
Therapies aimed at addressing schizophrenia symptoms can significantly improve outcomes.
Counseling and therapy help individuals understand their condition and cope with daily challenges.
Common therapies include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Supportive therapy
- Family therapy
- Social skills training
Therapy helps reduce symptoms, prevent relapse, and improve functioning.
- Rehabilitation & Social Support
Rehabilitation programs help patients:
- Learn job skills
- Improve communication
- Build daily living skills
- Reinforce social relationships
Support from family members is equally important in managing the condition.
A supportive environment can help mitigate the impact of schizophrenia symptoms.
- Hospitalization (When Needed)
During severe episodes, hospitalization may be necessary to ensure safety, stabilize symptoms, and adjust medications.
Living With Schizophrenia: Tips for Patients and Families
For Patients
- Stick to prescribed medication
- Maintain a routine
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Avoid alcohol and drugs
- Communicate openly with healthcare providers
- Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga or meditation
For Families
- Educate yourself about the disorder
- Offer emotional support without judgment
- Encourage treatment compliance
- Maintain a calm, structured home environment
- Attend family therapy if recommended
Families play a central role in recovery. A supportive, understanding environment can significantly reduce relapse rates.
Complications If Left Untreated
Without treatment, schizophrenia can lead to:
- Social isolation
- Relationship breakdown
- Unemployment
- Substance abuse
- Severe depression
- Risk of self-harm
Early intervention can prevent most of these complications.
Can Schizophrenia Be Prevented?
While there’s no guaranteed prevention, awareness of schizophrenia symptoms is vital.
There is no definitive way to prevent schizophrenia, but reducing risk factors can be helpful. Avoiding drug use, managing stress, and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits may reduce vulnerability.
Regular check-ups and early mental health support for individuals with high risk can also make a significant difference.
Conclusion
Schizophrenia is a serious but treatable mental health condition. With proper medical care, therapy, and social support, many individuals lead fulfilling lives. Breaking the stigma surrounding schizophrenia starts with awareness. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can empower families and communities to support those affected.
Empowering communities through knowledge of schizophrenia: symptoms can lead to better support for those affected.
If you or someone you know shows early signs, seeking timely help can change lives.
In conclusion, recognizing and understanding schizophrenia symptoms can save lives.
http://<a href=”https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schizophrenia”>WHO – Schizophrenia Facts</a>