Cerebral edema is a complex and serious condition in which excess fluid accumulates in the brain tissue, increasing the size of the brain and resulting in increased brain pressure. It may occur due to a number of reasons, which are explained in detail below:
Symptoms of Cerebral Edema:
- The headache is often very severe and persistent, usually felt throughout the head but sometimes concentrated in a specific area, worse on bending, coughing, or exercising.
- Nausea and vomiting: The headache is often accompanied by nausea; nausea may be followed by vomiting, often worse in the mornings, which may worsen on bending, coughing, or exercising.
- Changes in vision Double vision (diplopia) Seeing the same object twice, blurred or unclear vision, reduction or darkness in one field of vision, swelling of the veins behind the retina (papilledema), which can be seen during an eye examination.
- Confusion and loss of direction: A person may have difficulty understanding his or her surroundings, time and place, and recognizing his or her home, family, or friends.
- Speech difficulties: difficulty speaking, remembering words, forming sentences, slurred speech, or unclear speech.
- Walking difficulties: difficulty maintaining balance while walking, muscle weakness in one or more parts of the body, complete or partial paralysis of one or more parts of the body.
- Loss of alertness and loss of awareness: A person’s awareness is reduced, such as by drowsiness or sleepiness or complete or partial unconsciousness, in which the person is unable to respond.
Causes:
1.Head injury
Severe trauma: A severe blow to the head can cause swelling of brain tissue. This injury can be caused by accidents, sports injuries, or other accidental events.
Concussion and diffuse axonal injury: Even mild injuries can cause microscopic damage to brain tissue, leading to swelling.
2.Stroke
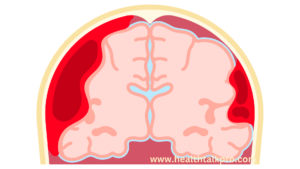 Ischemic stroke: A blockage of a blood vessel cuts off blood supply to a part of the brain, causing cells in that area to die and swelling.
Ischemic stroke: A blockage of a blood vessel cuts off blood supply to a part of the brain, causing cells in that area to die and swelling.
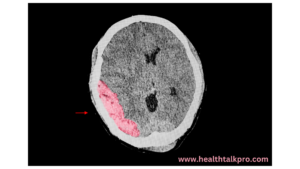
Hemorrhagic stroke: A rupture of a blood vessel causes bleeding in the brain, which can cause swelling in the surrounding tissues.
3.Tumors
Primary and metastatic tumors: Tumors that develop in the brain, whether they are primary or metastatic, can cause pressure and swelling in the surrounding tissues.
Swelling around the tumor: The area around the tumor may swell, which increases brain pressure.
4. Infection
Meningitis: infection of the meninges (the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord), caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal agents.
Encephalitis: infection of the brain, caused by viruses, bacteria, or other pathogens.
5. Hypoxia
 Lack of oxygen, also known as hypoxia, can result in brain cell damage and swelling. Suffocation, cardiac arrest, and various other conditions can lead to this condition. Lack of oxygen: Lack of oxygen (hypoxia) can cause brain cells to be damaged and swollen. This can be caused by suffocation, cardiac arrest, or other conditions.
Lack of oxygen, also known as hypoxia, can result in brain cell damage and swelling. Suffocation, cardiac arrest, and various other conditions can lead to this condition. Lack of oxygen: Lack of oxygen (hypoxia) can cause brain cells to be damaged and swollen. This can be caused by suffocation, cardiac arrest, or other conditions.
6. Hypertension
High blood pressure: Prolonged high blood pressure can put pressure on the brain’s blood vessels, causing them to leak and cause swelling.
Diagnosis of Cerebral Edema:
-
Computed Tomography Scan
A CT scan is a fast and accurate way to obtain images of the brain. This test is especially useful in emergency situations where a quick diagnosis is necessary.
- How it’s done: A CT scan uses a combination of X-rays and a computer. The patient lies on a table that goes inside the scanner, and the machine makes detailed images of the brain.
- Benefits: It helps detect bleeding, fractures, and other abnormalities early. CT scans can be done quickly and easily, which is very useful in emergency situations.
-
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
MRI is a more detailed and high-resolution imaging technique that helps detect soft-tissue abnormalities.
- How it’s done: MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves. The patient lies in a tube-like scanner, and the machine makes detailed images of the brain.
- Benefits: MRI helps better diagnose strokes, tumors, infections, and other soft-tissue abnormalities. It also provides a detailed view of the condition of blood vessels and nerves.
-
Lumbar Puncture or Spinal Tap
Lumbar puncture is a procedure in which a sample of the spinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid, CSF) is taken.
- How it is done: In this procedure, a sample of CSF is taken by inserting a needle into the spinal cord. It is usually done in the lower back.
- Benefits: Lumbar puncture helps diagnose infections such as meningitis or encephalitis. It is also helpful in checking the protein and glucose levels in the CSF.
-
Neurological tests
Neurological tests are done to evaluate the functional status of the brain and nervous system.
- How it is done: These tests involve checking muscle strength, sensation, coordination, and other neurological tests
- Benefits: Neurological tests provide a detailed evaluation of various functional conditions of the brain and nervous system; these tests help in accurately diagnosing various neurological abnormalities, such as stroke, tumor, infection, etc.
Treatment:
-
Mannitol or Hypertonic Saline
How it works:
- Both mannitol and hypertonic saline are osmotic diuretics that help reduce brain pressure.
- These drugs help remove excess fluid from brain tissue, thereby reducing swelling.
Uses:
- These drugs are usually given intravenously.
- Administration is done as per the dose and frequency prescribed by the doctor.
Benefits:
- Help reduce brain pressure rapidly.
- Are very useful in emergency situations.
-
Corticosteroids
How it works:
- Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory drugs.
- These drugs help reduce swelling in brain tissue, especially in cases of tumors or infections.
Uses:
- These drugs can be given orally or intravenously.
- Administration is done as per the dose and frequency prescribed by the doctor.
Benefits:
- Help reduce inflammation, especially in cases of tumors or infections.
- May be more effective in combination with other treatment methods.
-
Ventriculostomy
How it is done:
- Ventriculostomy is a surgical procedure in which a shunt is placed to drain excess fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) from the ventricles of the brain.
- This procedure helps reduce brain pressure.
Uses:
- When other treatment methods are not enough to reduce brain pressure.
- It can also be used in cases of hydrocephalus (excessive accumulation of fluid in the brain).
Benefits:
- Helps reduce brain pressure quickly and effectively.
- Can provide long-term relief in conditions such as hydrocephalus.
-
Surgery
- Surgery can play an important role in the treatment of cerebral edema, especially when other treatment methods are not enough or when the underlying cause needs to be addressed directly. Here is detailed information about surgery:
Tumor removal:
If the cause of cerebral edema is a tumor in the brain, surgery can be used to remove the tumor.
This procedure is performed by neurosurgeons and involves carefully separating brain tissue.
Removal of hemorrhage:
If the cause of cerebral edema is bleeding in the brain (hemorrhage), surgery can be used to remove the hemorrhage. • This procedure helps reduce brain pressure and prevent further damage.
Repair of vascular malformation or aneurysm:
If the cause of cerebral edema is a vascular malformation or aneurysm, surgery can be used to correct these abnormalities.
This procedure helps repair blood vessels and prevent future bleeding.
Uses:
In emergency situations:
When the patient’s condition is critical and other treatment methods are not sufficient.
In cases of tumors or hemorrhage:
When the tumor or hemorrhage needs to be removed.
In cases of vascular abnormalities:
When the vascular malformation or aneurysm needs to be repaired.
Benefits:
Surgery directly addresses the underlying cause, such as removing a tumor or hemorrhage.
Rapid relief:
Surgery can help reduce brain pressure quickly, which can improve the patient’s condition.
Long-term benefits:
Surgery can help prevent future damage, such as repairing a vascular malformation or aneurysm.
